How to Calculate Cell Potential Under Standard Conditions
2e I 2 s 2 I aq E. Write the oxidation and reduction half-reactions for the cell.
20 4 Cell Potential Under Standard Conditions Chemistry Libretexts
ΔGnFEcell where n is the number of moles of electrons transferred and F96500JVmol e is the Faraday constant.
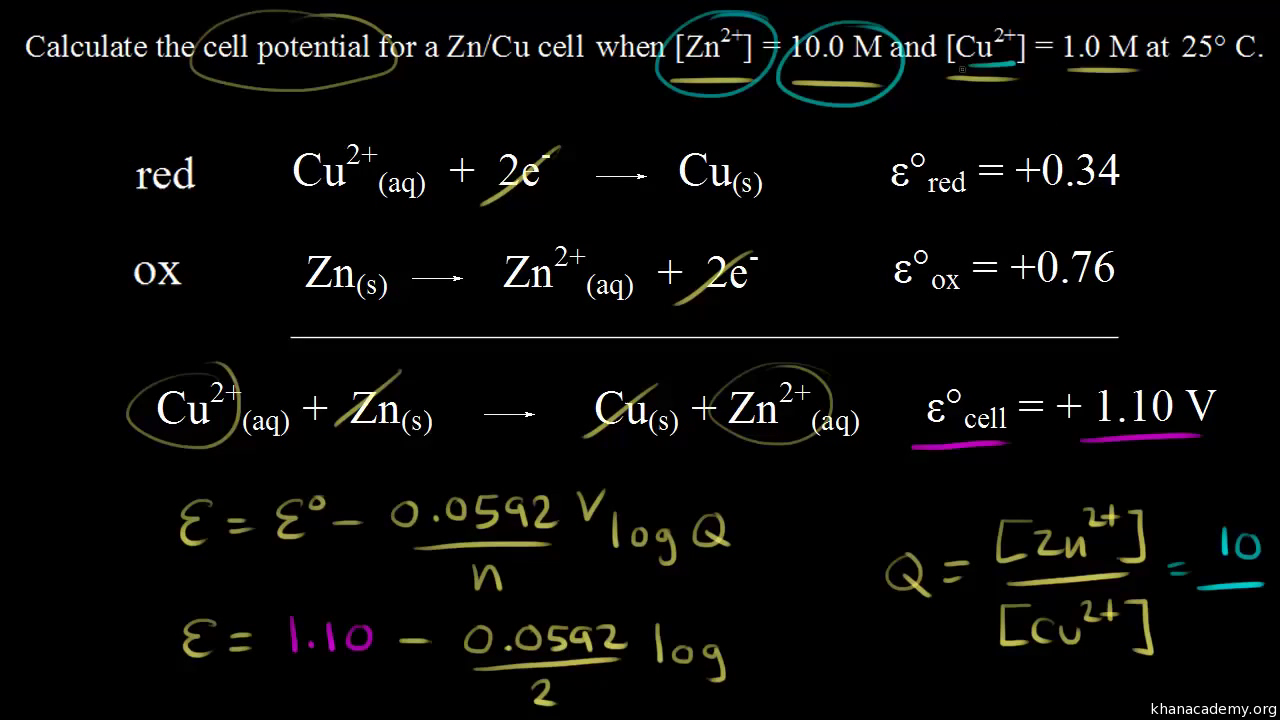
. The procedure is. Identify the anode and the cathode. 206 Cell Potentials Under Nonstandard Conditions.
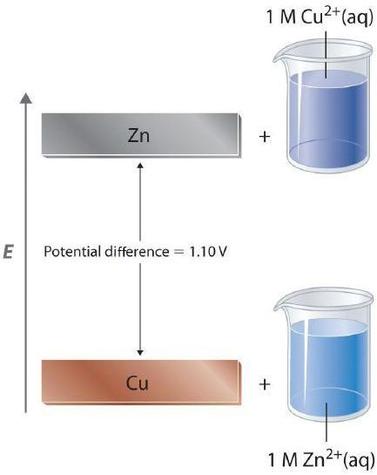
This implies that the potential difference between the Co and Cu electrodes is 110 V 051 V 059 V. Then we can calculate the standard electrode potential for the cell as follows E0 cell E0 cathode E0 anode E0 cell E0 Cu2 Cu - E0 Zn2 Zn if you use sign in place of in the equation then you have to write zinc electrode as oxidation electrode it means it will be written as E0 cell E0 Cu2 Cu E0 Zn2 Zn. Write cell representation cell reactions and find the EMF of the concentration cell.
Look up the reduction potential E⁰red for the reduction half-reaction in a table of reduction potentials Look up the reduction potential for the reverse of the oxidation half-reaction and reverse the sign to. In fact that is exactly the potential measured under standard conditions if a cell is constructed with the following cell diagram. M g2 aq 2 e- Mg s -237 V.
Cds MnO 2 s 4 H aq - Cd 2 aq Mn 2 aq 2 H2O l Given. Calculate the standard cell potential for the reaction E ocell using the tabled values. L ets calculate the potential generated in by a cell constructed from standard Zr and I 2 electrodes.
In order to calculate the standard potential we have to look up the half-reactions of copper and zinc. Calculate the cell potential for the following reaction under standard conditions. Calculate the standard cell potential at 25 C.
MnO 2 s 4 H aq 2e- - Mn 2 aq 2 H 2 O l E o 123 V. This problem has been solved. Standard electrode potentials reflect the relative oxidizing strength of the half-reactions reactant with stronger oxidants exhibiting larger more positive EX values.
E 293 V. Calculate the value for the reaction quotient Q. So if we add our standard reduction potential and our standard oxidation potential well get the standard cell potential.
Determine the new cell potential resulting from the changed conditions. Mgs 2Agaq Mg2aq 2Ags E cell 07996 V 2372 V 3172 V Mg s 2 Ag a q Mg 2 a q 2 Ag s E cell 07996 V 2372 V 3172 V Key Concepts and Summary. This relationship referred to as the Nerst equation will allow us to calculate the cell.
The values below in parentheses are standard reduction potentials for half-reactions measured at 25 C 1 atmosphere and with a pH of 7 in aqueous solution. We calculate Q using molar concentrations for solutions and. So the standard potential for the cell so E zero cell is equal to 54 plus 166 which is equal to 220 volts.
List the known values and plan the problem. From the table we write a balanced reduction half-reaction for each electrode and copy down the reduction potentials. All the calculations to this point have been calculated under standard conditions.
So that would be positive 54 volts so positive 54 plus 166 plus positive 166 volts. Write the balanced equation for the overall cell reaction that occurs. To find the EMF of a concentration element you must use the following formula.
Stay tuned with BYJUS for more such interesting articles. How to Calculate Standard Cell Potential Eocell ε ε cat - ε an OR ε εred εox Zn 2 Co Zn Co 2 ε 2Cr 3 3Cu 2Cr 3Cu 2 ε What is the balanced reaction for the galvanic cell composed of Mn 2 Mn and Fe 2 Fe half cells and calculate its standard cell potential. See the answer See the answer done loading.
Co s Co2 aq 1M Cu2 aq 1M Cus E 059V This cell diagram corresponds to the oxidation of a cobalt anode and the reduction of Cu 2 in solution at the copper cathode. E cell cell potential under nonstandard conditions V E 0 cell cell potential under standard conditions R gas constant which is 831 volt-coulombmol-K T temperature K n number of moles of electrons exchanged in the electrochemical reaction mol F Faradays constant 96500 coulombsmol Q reaction quotient which is the equilibrium. The polarity of the cell is determined by knowing that zinc metal is a.
Known begin alignE0_ text Ag080 text Vend align. Mg s Cu2 aq Cu s Mg2 aq Cu2 aq 2 e- Cu s 034 V. When the half-cell is operating under standard state conditions its potential is the standard electrode potential E X.
Calculate the standard cell potential of a voltaic cell that uses the AgAg and SnSn 2 half-cell reactions. In fact that is exactly the potential measured under standard conditions if a cell is constructed with the following cell diagram. Calculate the cell potential of this reaction under standard reaction conditions.
CH 3 COOH 2H 2e CH 3 CHO H 2 O -058 2H 2 e H 2 00 O 2 2H 2e H 2 O 2 07 O 2 4H 4e 2H 2 O 164. When the concentrations of the solutions in the anode and cathode compartment are changed the cell potential will change. ThereforeE 008 V.
E cell E 0cell - RTnF x lnQ E cell 0277 V - 0013 V x ln 0100 E cell 0277 V - 0013 V x -2303 E cell 0277 V 0023 V E cell 0300 V Answer The cell potential for the two reactions at 25 C and Cd 2 0020 M and Pb 2 0200 M is 0300 volts. Up to 10 cash back Calculate the standard cell potential of the following reaction. The standard cell potential for the reaction is then 034 V -076 V 110 V.
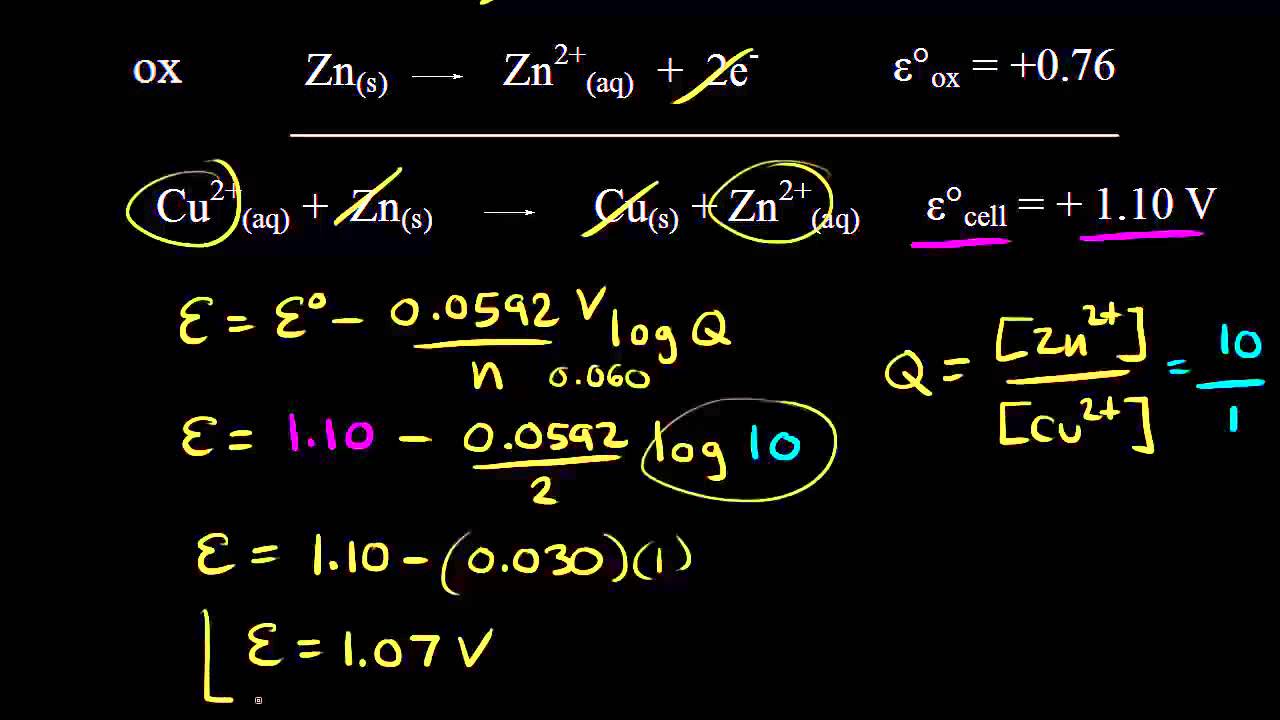
Using The Nernst Equation Video Khan Academy

20 4 Cell Potential Under Standard Conditions Chemistry Libretexts

No comments for "How to Calculate Cell Potential Under Standard Conditions"
Post a Comment